Client Sector
Manufacturing/Industrial Process
Expertise
Building Materials
Location
Dearborn, MI
Manufacturing/Industrial Process
Ford Tunnel Condition Assessment
SME conducted a structural condition assessment of the Pedestrian and Steam and Condensate Distribution System (SCDS) tunnel at Ford Motor Company’s Research and Engineering Center (REC) in Dearborn, Michigan.
SME assessed cast-in-place reinforced concrete tunnel elements to determine the severity and extent of visually evident distresses. Limited nondestructive testing (NDT) was conducted at representative locations to estimate the remaining service life of existing reinforced concrete elements.
Tunnel elements were evaluated and categorized with respect to condition and type of deterioration. To assist in the development of repair plans, concrete distress conditions were assigned a Priority Rating Value based on severity. Tunnel distresses were mapped and compiled into master diagrams and an Excel spreadsheet, which included internal links to a photo of each distress condition.
Assessment activities were based on: visual assessment of accessible areas in accordance with ACI guidelines; physical assessment using acoustical sounding in accordance with ASTM guidelines; NDT testing of tunnel walls, and ceiling and floor slab areas to measure concrete thickness; internal distress conditions; and location of embedded reinforcing steel.
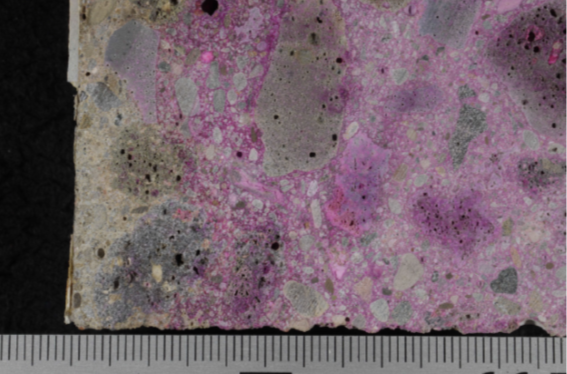
Sixteen concrete core samples were extracted in pedestrian and utility portions of the tunnel. These areas were first scanned with GPR to detect reinforcing bar locations to avoid cutting them during coring. Two concrete cores were subjected to a concrete service life analysis using service life modeling software. Chloride Ion testing and petrographic analysis were conducted on two cores where carbonation was detected by phenolphthalein staining and signs of distress in the form of cracks associated with alkali-silica reaction (ASR).
Based on the finding of the assessment, SME provided repair recommendations to increase the tunnel’s service life an additional 30 years.